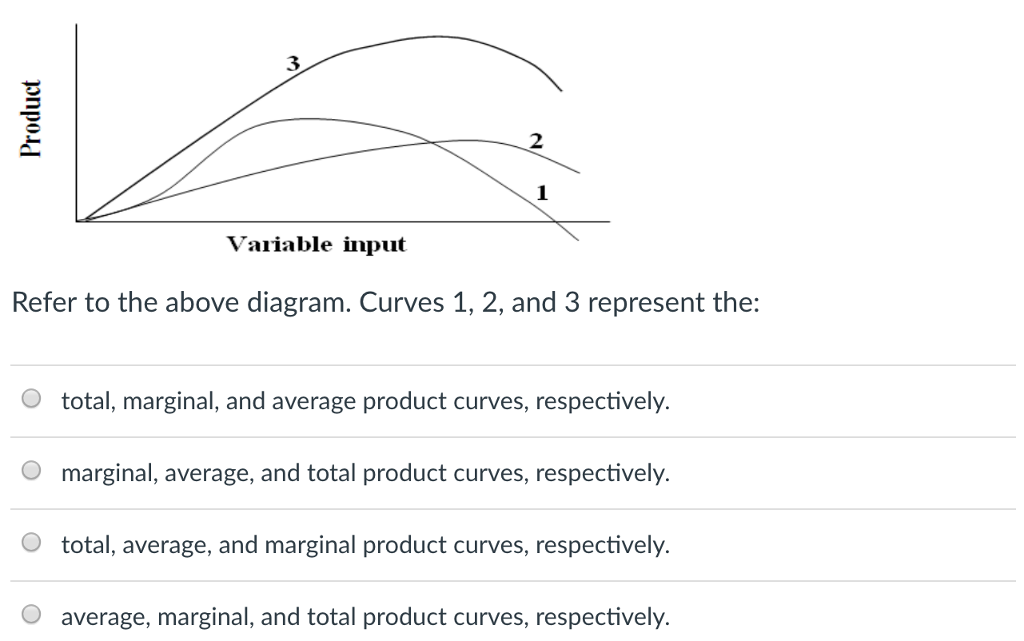
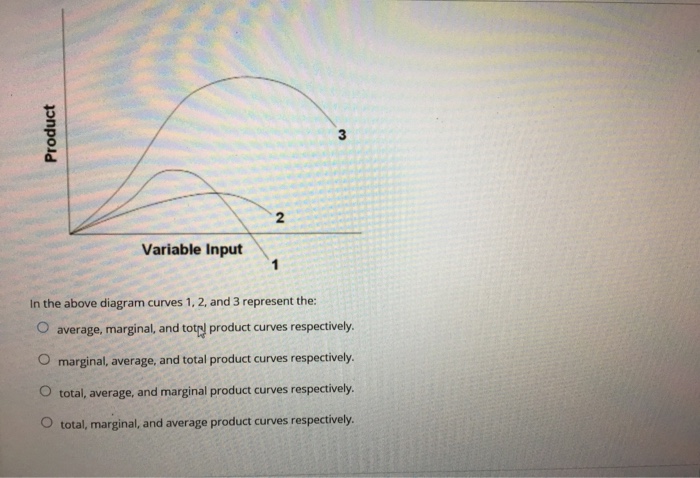
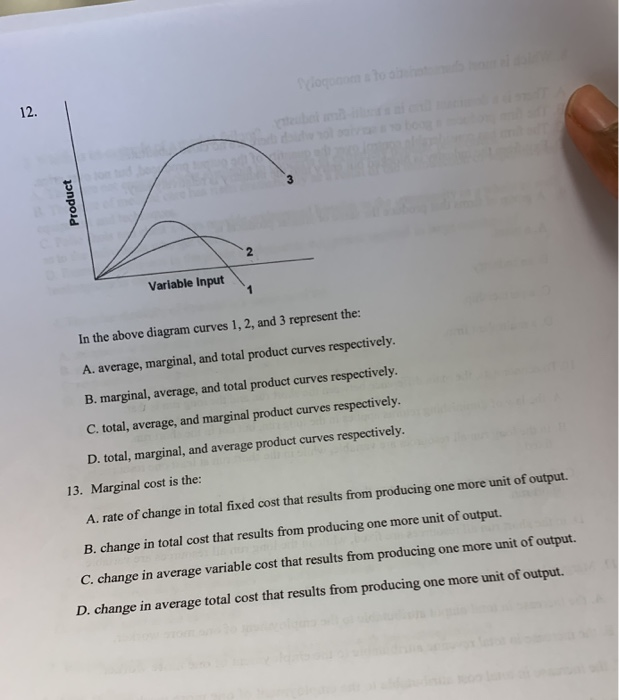
37 in the diagram, curves 1, 2, and 3 represent
Figure shows four PV diagrams. Which of these curves ... Which of these curves represent isothermal and adiabatic processes respectively? Solve Study Textbooks Guides. Join / Login >> Class 11 ... Process 1, 2 and 3 are respectively. Medium. View solution > The P-T diagram for an ideal gas is shown in the figure, where AC is an adiabatic process. The corresponding PV diagram is. 24 In the above diagram curves 1 2 and 3 represent the A ... 24 In the above diagram curves 1 2 and 3 represent the A average marginal and. 24 in the above diagram curves 1 2 and 3 represent. School University of Tunku Abdul Rahman; Course Title ECON FHBM1014; Uploaded By DoctorCaribou179. Pages 8 This preview shows page 6 - 8 out of 8 pages.
In the above diagram curves 1 2 and 3 represent the A ... 47. In the above diagram curves 1, 2, and 3 represent the: A) average, marginal, and total product curves respectively. B) marginal, average, and total product curves respectively. C) total, average, and marginal product curves respectively. D) total, marginal, and average product curves respectively. Answer: B.
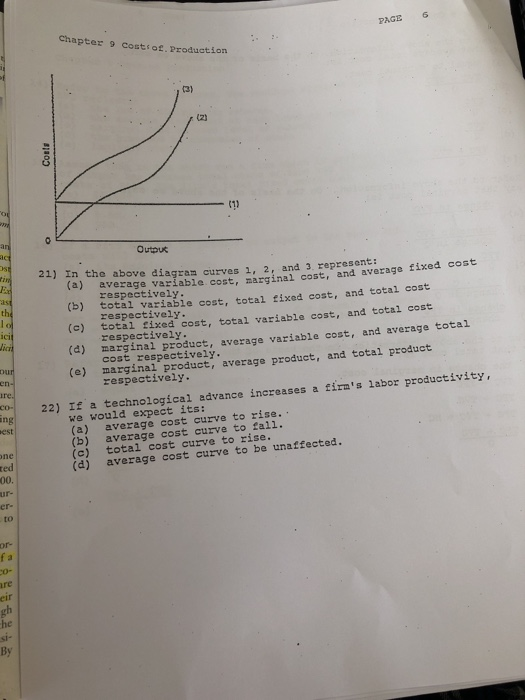
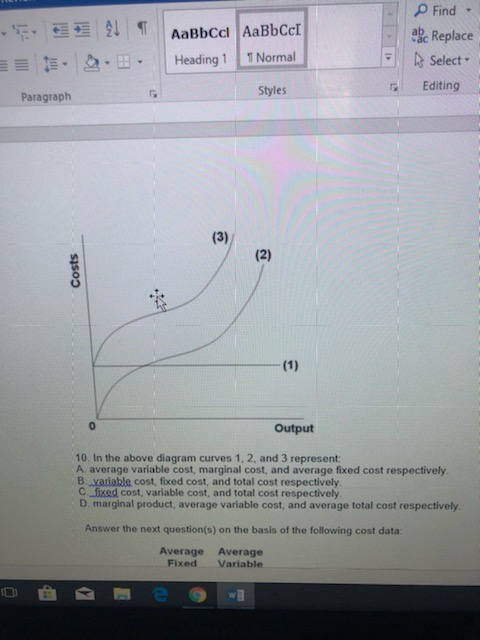
In the diagram, curves 1, 2, and 3 represent
Solved Output In the diagram, curves 1, 2, and 3 represent ... Output In the diagram, curves 1, 2, and 3 represent: total variable cost, total fixed cost, and total cost respectively. average variable cost, marginal cost, and average fixed cost respectively. O marginal product, average variable cost, and average total cost respectively. total fixed cost, total variable cost, and total cost respectively. PDF Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge ... 7 The diagram shows the relationship between total expenditure and price for three products, 1, 2 and 3. total expenditure price O 1 2 3 Which curves represent the products with price elastic and unitary price elastic demand? elastic unitary A 1 2 B 2 3 C 3 1 D 3 2 8 A firm has a perfectly elastic supply curve at the market price of $10. ECON 202 Blanchard Exam 2 - Subjecto.com In the diagram, curves 1, 2, and 3 represent: a. average variable cost, marginal cost, and average fixed cost respectively. b. total variable cost, total fixed cost, and total cost respectively. c. total fixed cost, total variable cost, and total cost respectively. d. marginal product, average variable cost, and average total cost respectively.
In the diagram, curves 1, 2, and 3 represent. 9. In the above diagram curves 1, 2, and 3 represent the ... In the above diagram curves 1, 2, and 3 represent the: A. average, marginal, and total product curves respectively. B. marginal, average, and total product curves respectively . C. total, average, Just from $13/Page. Order Essay . Continue to order Get a quote. Post navigation. MICROECONOMICS QUIZ 5 Flashcards | Quizlet The above diagram suggests that: curves 1, 2, and 3 represent the: when marginal product lies above average product, average product is rising Suppose that a business incurred explicit costs of $1 million and implicit cost of $200,000 in a specific year. In the above diagram curves 1 2 and 3 represent the A ... 11. In the above diagram curves 1, 2, and 3 represent the: A) average, marginal, and total product curves respectively. B ) marginal, average, and total product curves respectively. C) total, average, and marginal product curves respectively. D) total, marginal, and average product curves respectively. 12. How to Tell If a Graph Represents a Function A curve drawn in a graph represents a function, if every vertical line intersects the curve in at most one point. Question 1 : Determine whether the graph given below represent functions.
PDF the TYPES of questions you will have on your Unit 1, 2 ... Unit 1, 2 & 3 Exam Practice Unit 1-3 Exam Practice Page 6 Base your answers to questions 39 through 42 on the information below. Given the heating curve where substance X starts as a solid below its melting point and is Solved In the diagram, what do Curves 1, 2, and 3 ... In the diagram, what do Curves 1, 2, and 3 represent? a. Average, marginal, and total product respectively b. Marginal, average, and total product respectively c. Total, average, and marginal product respectively d. Total, marginal, and average product respectively; Question: In the diagram, what do Curves 1, 2, and 3 represent? a. PDF Important Questions Unit 1 Introduction [6 Marks] 1. 2. 3 ... Why MR Curve of a price taking firm is perfectly elastic and equal to AR? (Use diagram) 41. ... Construct a pie diagram to represent the cost of construction of a house in Delhi Items Expenditure (in%) Labour 25 ... Capital goods 0.3 Others 2.0 100 32. Represent the following data with the help of suitable bar diagram : Year 2009 2010 2011 2012 Microeconomics: Chapter 9 Flashcards - Quizlet In the diagram, curves 1, 2, and 3 represent the: marginal, average, and total product curves respectively. In the figure, curves 1, 2, 3, and 4 represent the: MC, ATC, AVC, and AFC curves respectively. The diagram suggests that: when marginal product lies above average product, average product is rising.
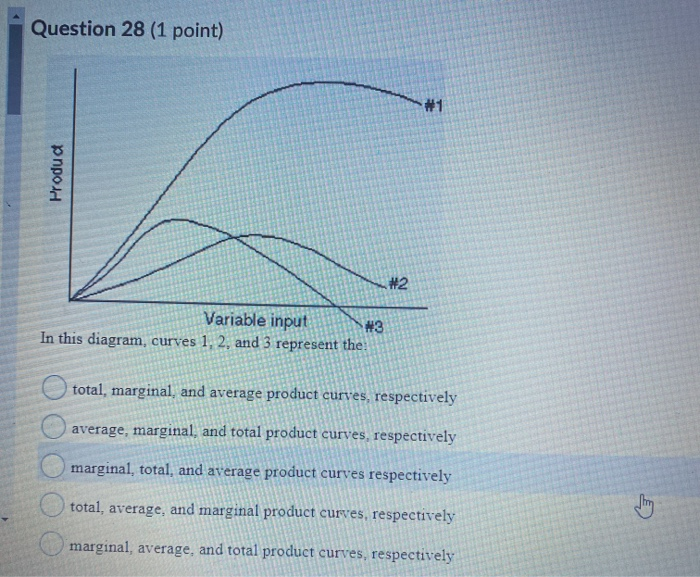
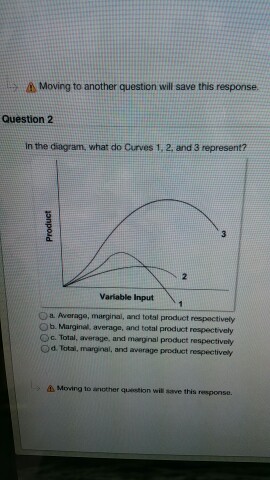
[Solved] #1 #2 Variable input In this diagram, curves 1, 2 ... Answer to #1 #2 Variable input In this diagram, curves 1, 2, and 3 represent the: #3 O total, marginal, and average product curves, respectively total, average, and margi | SolutionInn revcosts In the above figure, curves 1, 2, 3, and 4 represent the: A. ATC, MC, AFC, and AVC curves respectively. B. AFC, MC, AVC, and ATC curves respectively. ... The above diagram shows the short-run average total cost curves for five different plant sizes of a firm. In ... A cyclic process ABCD is shown in the P-V diagram. Which ... A cyclic process ABCD is shown in the P-V diagram. Which of the following P-T curves represent the same process ? (1) (2) (3) (4) Practice questions, MCQs, Past Year ... 24 In the above diagram curves 1 2 and 3 represent the A ... In the above diagram curves 1 , 2 , and 3 represent the : A. average , marginal , and total product curves respectively . B. marginal , average , and total product curves respectively .
Heating Curves and Phase Diagrams (M11Q2) - UW-Madison ... Figure 2. A heating curve and phase diagram for water. Solution. While anywhere along the line segment BD represents a phase change from solid to liquid, and points Y and Z are both on that line, the correct answer is D. At point Y, the phase change is occurring at the same pressure (1 atm) that was used to construct the heating curve.
Study 61 Terms | Economics Flashcards | Quizlet In the diagram, curves 1, 2, and 3 represent the: marginal, average, and total product curves respectively. The basic difference between the short run and the long run is that: at least one resource is fixed in the short run, while all resources are variable in the long run.
Econ Exam 2 Flashcards - Quizlet In the above diagram curves 1, 2, and 3 represent the: marginal, average, and total product curves respectively. As the firm in the above diagram expands from plant size #3 to plant size #5, it experiences: economies of scale. Use the following data to answer the next question(s). The letters A, B, and C designate three successively larger ...
PDF UNIT 1 Microeconomics - Online Campus 1 Part C Use Figure 2.6 to answer the next five questions. Each question starts with Curve BB' as a country 's production possibilities curve. 3. Suppose there is a major technological breakthrough in the consumer-goods industry, and the new technology is widely adopted. Which curve in the diagram would represent the new produc-tion ...
Microeconomics (ECON-2302) Flashcards | Quizlet In the above diagram curves 1, 2, and 3 represent: ~ average variable cost, marginal cost, and average fixed cost respectively. ~ total variable cost, total fixed cost, and total cost respectively. ~ total fixed cost, total variable cost, and total cost respectively. ~ marginal product, average variable cost, and average total cost respectively.
A typical UCST-type phase diagram, curve 1, curve 2 and ... Download scientific diagram | A typical UCST-type phase diagram, curve 1, curve 2 and curve 3 represent crystallization temperature curve, spinodal curve and binodal curve, respectively from ...
PDF 9709 32 June20 - GCE Guide 3 2 x lny O 1.5,1.2 5.24,2.7 The variables xand ysatisfy the equation y2 = Aekx, where Aand kare constants.The graph of lnyagainst xis a straight line passing through the points 1.5, 1.2 and 5.24, 2.7 as shown in the diagram. Find the values of Aand kcorrect to 2 decimal places.[5]
In this diagram curves 1 2 and 3 represent the A average ... In this diagram curves 1 2 and 3 represent the A average marginal and total. In this diagram curves 1 2 and 3 represent the a. School Cambridge College; Course Title ECONOMIC 103; Type. Homework Help. Uploaded By zhongyi11; Pages 4 This preview shows page 2 - 4 out of 4 pages.
ECON 202 Blanchard Exam 2 - Subjecto.com In the diagram, curves 1, 2, and 3 represent: a. average variable cost, marginal cost, and average fixed cost respectively. b. total variable cost, total fixed cost, and total cost respectively. c. total fixed cost, total variable cost, and total cost respectively. d. marginal product, average variable cost, and average total cost respectively.
PDF Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge ... 7 The diagram shows the relationship between total expenditure and price for three products, 1, 2 and 3. total expenditure price O 1 2 3 Which curves represent the products with price elastic and unitary price elastic demand? elastic unitary A 1 2 B 2 3 C 3 1 D 3 2 8 A firm has a perfectly elastic supply curve at the market price of $10.
Solved Output In the diagram, curves 1, 2, and 3 represent ... Output In the diagram, curves 1, 2, and 3 represent: total variable cost, total fixed cost, and total cost respectively. average variable cost, marginal cost, and average fixed cost respectively. O marginal product, average variable cost, and average total cost respectively. total fixed cost, total variable cost, and total cost respectively.




















0 Response to "37 in the diagram, curves 1, 2, and 3 represent"
Post a Comment