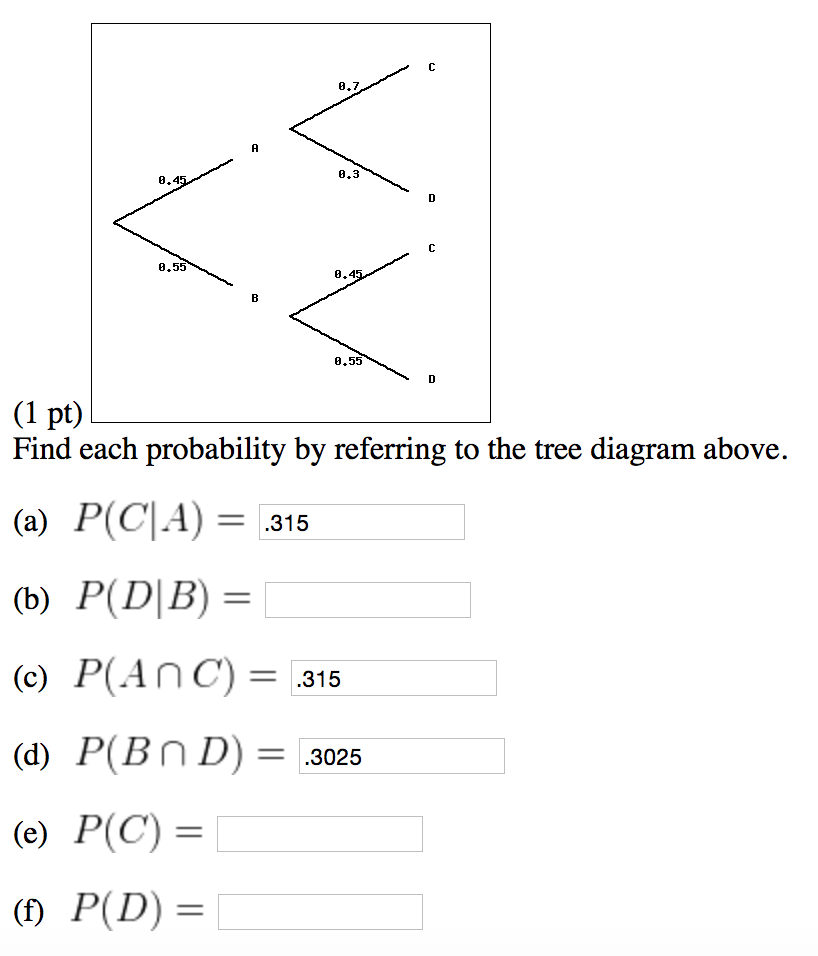
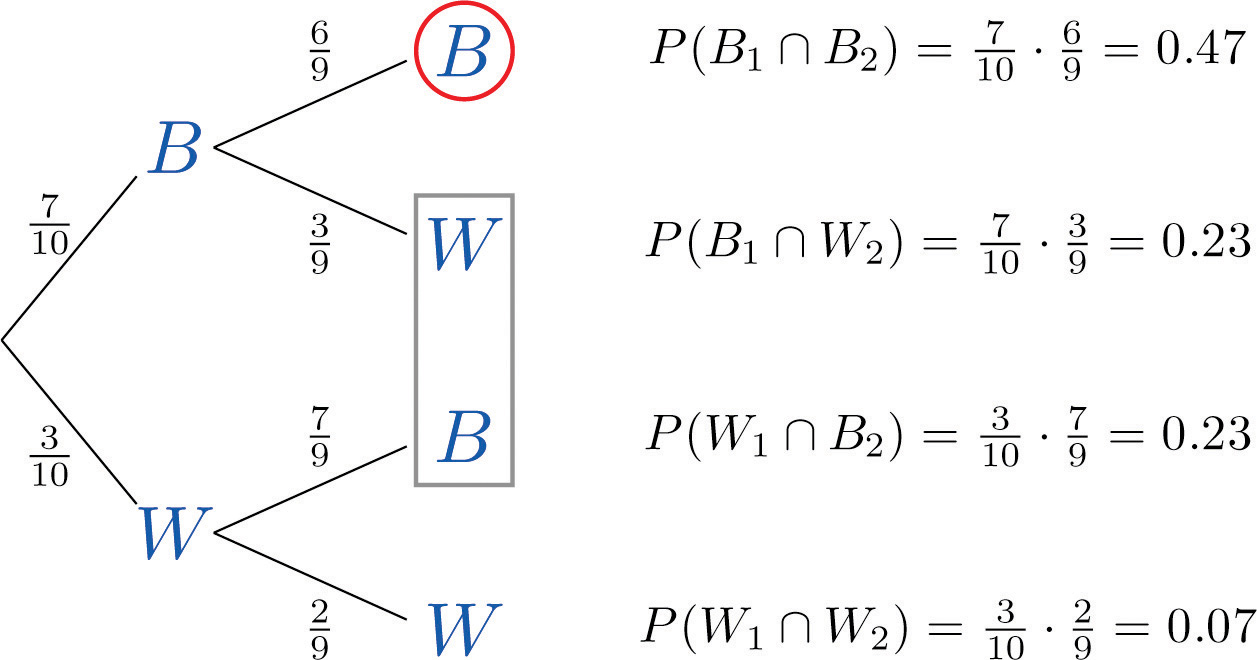
37 find each probability by referring to the tree diagram above.
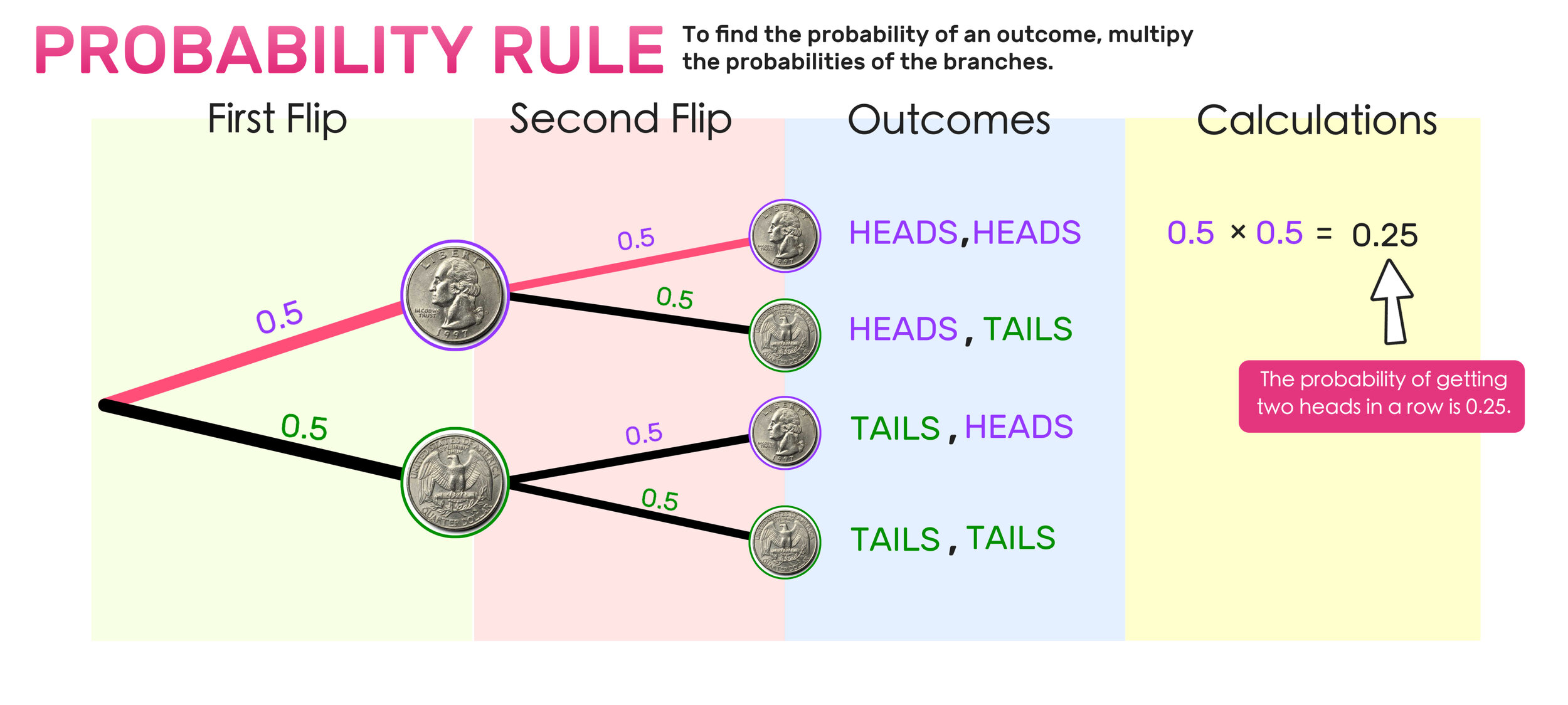
XLS JustAnswer It is difficult to draw, so I will enter the data. A=0.75 B=0.25 C=0.9 D=0.1 C=0.3 D=0.7 Find each probability by referring to the tree diagram: a) P(C given A)= b) P(D given B)= c) P( A and C)= d) P(B and D)= e) P(C)= F P (D)= Republican Democrat Independent Total Male Female A person is randomly selected. What is the probability that the person is: PowerPoint Presentation Probability Trees. We saw probability trees in Year 1. The only difference here is . determining a conditional probability . using your tree. Example: You have two bags, the first with 5 red balls and 5 blue balls, and the second with 3 red balls and 6 blue balls. You first pick a ball from the first bag, and place it in the second.
SOLVED:Find each probability by referring to the tree ... Find each probability by referring to the tree diagram above: (a) P(CIA) = (6) P(DIB) = (c) P(Anc) -L (d) P(Bn D) = (e) P(C) = (0) P(D) = Get the answer to your homework problem. Try Numerade Free for 30 Days

Find each probability by referring to the tree diagram above.
Finding Probability Using a Tree Diagram - onlinemath4all Step 1 : Make a tree diagram to find the sample space for the compound event. Step 2 : Find the number of possible outcomes in the sample space. From the above tree diagram, number of possible outcomes in the sample space is 12. Step 3 : Find the number of possible outcomes for turkey and Swiss on wheat bread. PDF X AP Statistics Solutions to Packet 7 case, the probabilities in (c) and (d) are the same because the events differ by 2 individual values, 0.3 and 0.5, each of which has probability 0. 7.7 CONTINUOUS RANDOM VARIABLE, II Let the random variable X be a random number with the uniform density curve as in the previous exercise. Find the following probabilities: (a) P(X ≤ 0.49) = 0.49 Probability Questions | Probability Questions with Solutions Find the probability of each event to occur. Solution: Let us say the events of getting two heads, one head and no head by E 1, E 2 and E 3, respectively. P (E 1) = 105/500 = 0.21. P (E 2) = 275/500 = 0.55. P (E 3) = 120/500 = 0.24. The Sum of probabilities of all elementary events of a random experiment is 1.
Find each probability by referring to the tree diagram above.. Probability Tree Diagrams - mathsisfun.com The tree diagram is complete, now let's calculate the overall probabilities. This is done by multiplying each probability along the "branches" of the tree. Here is how to do it for the "Sam, Yes" branch: (When we take the 0.6 chance of Sam being coach and include the 0.5 chance that Sam will let you be Goalkeeper we end up with an 0.3 chance.) Tree diagrams and conditional probability - Khan Academy Starting a tree diagram. The chance that the alarm is triggered depends on whether or not the bag contains a forbidden item, so we should first distinguish between bags that contain a forbidden item and those that don't. "Suppose that of bags contain forbidden items." Created with Raphaël. Forbidden Not forbidden. Probability Statistics for Engineers Scientists Figure 2.6: Tree diagram for Example 2.14. Solution : Since n 1 = 4 and n 2 = 3, a buyer must choose from n 1 n 2 = (4)(3) = 12 possible homes. The answers to the two preceding examples can be verified by constructing tree diagrams and counting the various paths along the branches. For instance, 46 Chapter 2 Probability PDF Geometry Semester Exam Review Packet Chapter 1 Find the probability that the rat will go into room B in the diagram below. 28. Find the perimeter of each shape below. Assume the diagram in part (b) is a parallelogram. a. b. c. 29. Use the triangles to the right to answer the following questions. a. Are the triangles at right similar? How do you know? Show your reasoning in a flowchart.
PDF David A. Baum, Stacey DeWitt Smith, Samuel S. Donovan 10) In the above tree, assume that the ancestor was an herb (not a tree) without leaves or seeds. Based on the tree and assuming that all evolutionary changes in these traits are shown, which of the tips has a tree habit and lacks true leaves? a) Lepidodendron b) Clubmoss c) Oak d) Psilotum e) Fern 'a' is the correct answer. Clubmosses are ... SOLVED:point) Find each probability by referring to the ... Fill scandal. I'm categorize Giger license. You know, license driver may. Okay, so get home part. See the cage arms apu targa fartsy is that it is asking about the Soviet off your city and town and finding the probability accordingly for the licence driver again. So let's considered bait does okay, G 50% is I don't on 50% on minor in the city. PDF 1 Markov Chains - Social Science Computing Cooperative Using the probability tree diagram, we can now begin to answer the questions posed above. By assumption, the process starts in state 2 in period 0. Following one of the two branches from this initial node, the process then occupies either state 2 (with probability 1/2) or state 3 (with probability 1/2) in period 1. Of course, we PDF Probability Topics: Contingency Tables - Saylor Academy Find the probability that a person is male given that the person prefers hiking near lakes and ... so the probability of choosing each door is 1 3. Door Choice ... ouY could also do this problem by using a probability tree. See the reeT Diagrams (Op-tional) 1 section of this chapter for examples. 1 "Probability opics: ...
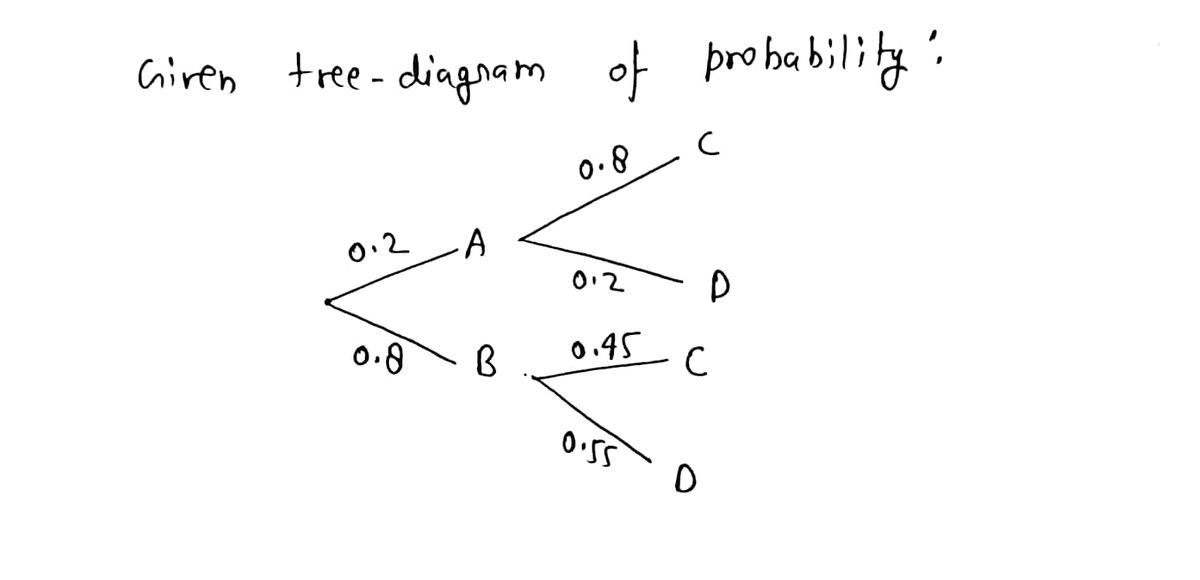
PDF Homework Example from ACE: What Do You Expect ... organized list. From the above tree we have the list of equally likely outcomes, starting at the top of the tree: B1, B2, B3, B3, R1, R2, R3, R3, R1, R2, R3, R3, G1, G2, G3, G3, Y1, Y2, Y3, Y3. There are 20 possibilities. Four of them are R3. The probability of a red on X and a 3 on Y is 4 20. 11. Raymundo invented the Prime Number Multiplication Game. [Solved] In" (6 points) Find each probability by ... Based on the tree diagram, we can easily see that on the first column of tree the probability of A is 2/5 which can be written as P r (A) = 5 2 the probability of B is 3/5 which can be written as P r (B) = 5 3 Now, on the second column of tree diagram, this is a conditional probability, given that A occur, the probability of having C is 3/4. We can write this as P r (C ∣ A) = 4 3 given that A occur, the probability of having D is 1/4. Find each probability by referring to the tree diagram ... Answer to: Find each probability by referring to the tree diagram above. a). P ( C | A ) = b). P ( D | B ) = c). P ( A ? C ) = d). P ( B ? D... Solved Find each probability by referring to the tree ... Statistics and Probability questions and answers Find each probability by referring to the tree diagram above. (a) 𝑃(𝐶|𝐴)= (b) 𝑃(𝐷|𝐵)= (c) 𝑃(𝐴∩𝐶)= (d) 𝑃(𝐵∩𝐷)= (e) 𝑃(𝐶)= (f) 𝑃(𝐷)=
Thinking About Probability Trees - Pondering Planning in ... The numbers above were modelled roughly on the probability tree from the question below. While the frequency tree looks at observed data for many people playing the games, the probability tree looks at the theoretical probabilities for each individual person playing the games.
Solved Find each probability by referring to the tree ... Math. Statistics and Probability. Statistics and Probability questions and answers. Find each probability by referring to the tree diagram above. (a) P (C|A) = (b) P (D|B) = (c) P (A intersection C) = (d) P (B intersection D) = (e) P (C) = (f) P (D) =.
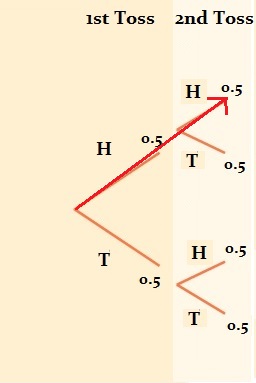
Basic Probability Rules » Biostatistics » College of ... Remember, since H and T are equally likely on each toss, and since there are 8 possible outcomes, the probability of each outcome is 1/8. See if you can answer the following questions using the diagrams and/or the list of outcomes for each event along with what you have learned so far about probability.
Answered: Find each probability by referring to… | bartleby Find each probability by referring to the tree diagram above. (a) P (C\A) = 0.45 (b) P (D\B) = 0.65 (c) P (AnC) = 0.09 (d) P (Bn D) = (e) P (C) = (1) P (D) =.
PDF 1 Math 1313 Section 6.6 Section 6.6 - Bayes' Theorem the two tosses. Find the probability distribution for X and then draw the histogram corresponding to the probability distribution of X. Popper 5: Using the information from the above problem, Find the P(X < 1) a. 0.250 b. 0.500 c. 0.750 d. 1.000
Find each probability by referring to the tree diagram ... View this answer. From tree diagram, we have P (A) P ( A) = 0.15, P (B) P ( B) = 0.85, P (C/A) P ( C / A) = 0.9, P (D/A) P ( D / A) = 0.1, P (C/B) P ( C / B) =... See full answer below.
Probability Tree Diagrams (video lessons, examples and ... We can construct a probability tree diagram to help us solve some probability problems. A probability tree diagram shows all the possible events. The first event is represented by a dot. From the dot, branches are drawn to represent all possible outcomes of the event. The probability of each outcome is written on its branch. Example:
Answered: Find each probability by referring to… | bartleby Solution for Find each probability by referring to the tree diagram above. (a) P(C\A) (b) P(D\B) = (C) P(AnC) = close. Start your trial now! First week only $4.99! arrow_forward. learn. write. tutor. study resourcesexpand_more. Study Resources. We've got the study and writing resources you need for your assignments. ...
2020W2_STAT_251_201_2020W.FDWRAZ5TX302.Assignment-02.pdf ... Find each probability by referring to the tree diagram above. (a) P ( C. |. A ) = (b) P ( D. |. B ) = Plant A1. 7. (2 points) Items in your inventory are produced at three different plants: 50% from plant A1, 30% from plant A2 and 20% from plant A3.
[Solved] Find the probabilities in Problem by referring to ... Find the probabilities in Problem by referring to the following Venn diagram and using Bayes' formula (assume that the simple events in S are equally likely):
Probability Questions | Probability Questions with Solutions Find the probability of each event to occur. Solution: Let us say the events of getting two heads, one head and no head by E 1, E 2 and E 3, respectively. P (E 1) = 105/500 = 0.21. P (E 2) = 275/500 = 0.55. P (E 3) = 120/500 = 0.24. The Sum of probabilities of all elementary events of a random experiment is 1.
PDF X AP Statistics Solutions to Packet 7 case, the probabilities in (c) and (d) are the same because the events differ by 2 individual values, 0.3 and 0.5, each of which has probability 0. 7.7 CONTINUOUS RANDOM VARIABLE, II Let the random variable X be a random number with the uniform density curve as in the previous exercise. Find the following probabilities: (a) P(X ≤ 0.49) = 0.49
Finding Probability Using a Tree Diagram - onlinemath4all Step 1 : Make a tree diagram to find the sample space for the compound event. Step 2 : Find the number of possible outcomes in the sample space. From the above tree diagram, number of possible outcomes in the sample space is 12. Step 3 : Find the number of possible outcomes for turkey and Swiss on wheat bread.








/TreeDiagram2-c209ffffddd14e989cd72e9c38e518f0.png)





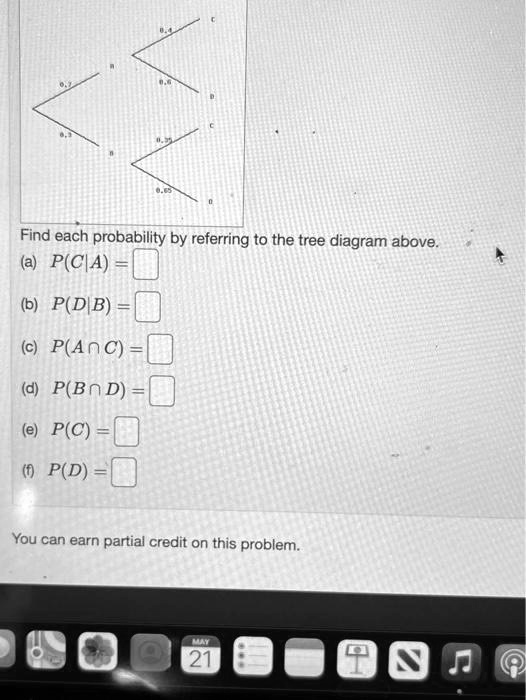


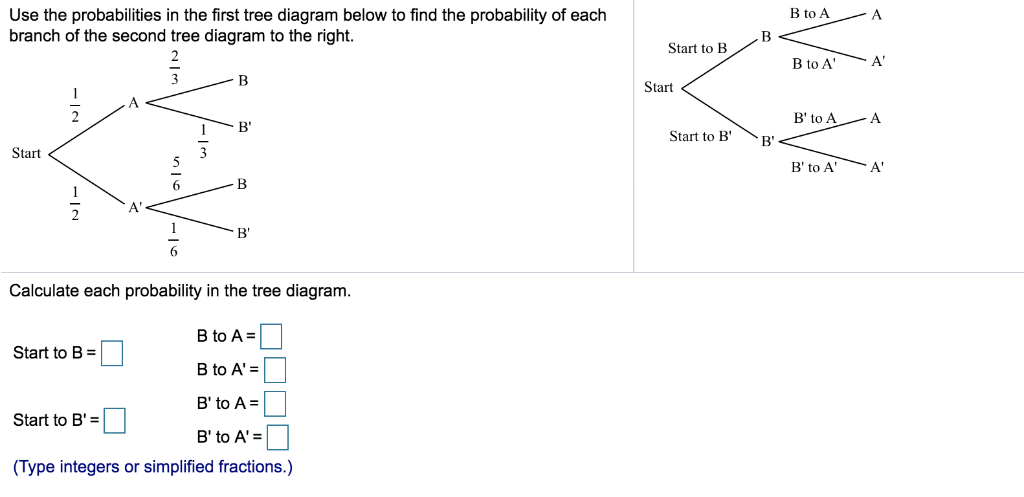



0 Response to "37 find each probability by referring to the tree diagram above."
Post a Comment