36 cardiac muscle cell diagram
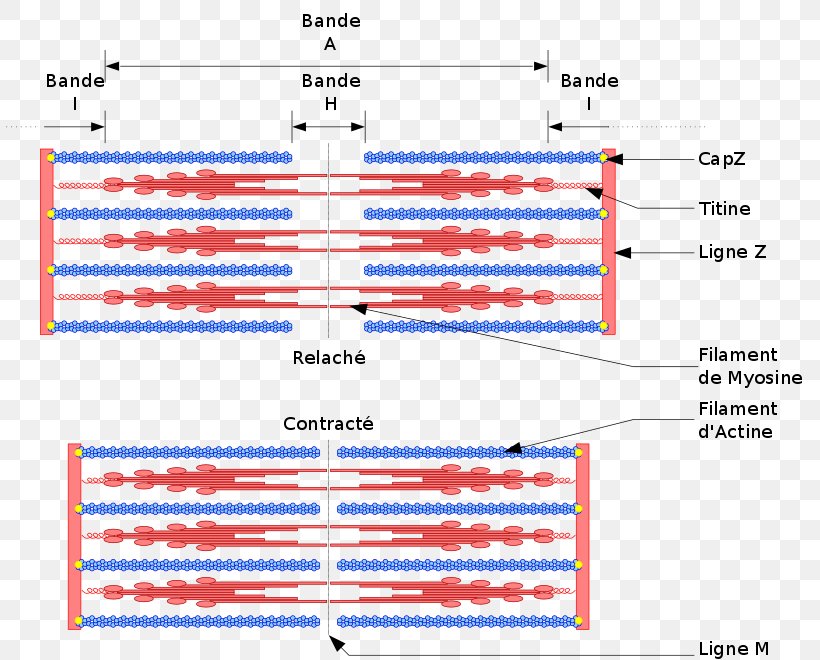
Anatomy, Thorax, Cardiac Muscle - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf The individual cardiac muscle cell (cardiomyocyte) is a tubular structure composed of chains of myofibrils, which are rod-like units within the cell. The myofibrils consist of repeating sections of sarcomeres, which are the fundamental contractile units of the muscle cells. Cardiac Muscle Cell - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Figure 5 shows a diagram of how calcium activates the cardiac muscle cell to contract. There are three pools of Ca 2+ that are important to the cardiac muscle cell: the extracellular fluid, the SR, and the cytoplasm. Only Ca 2+ in the latter compartment is able to bind with the troponin-binding sites and initiate contraction.
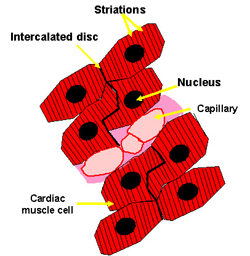
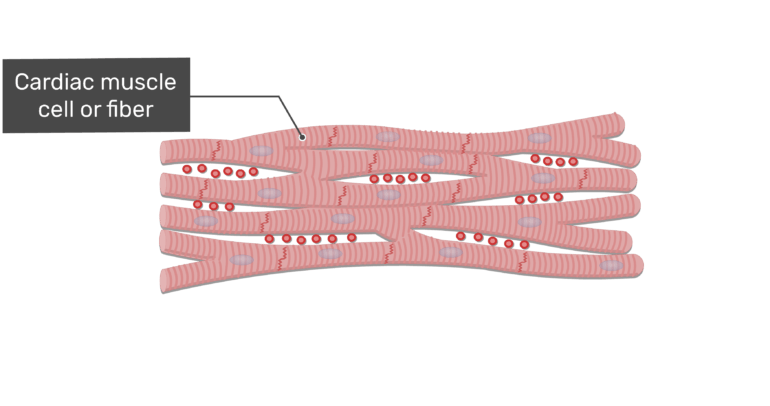
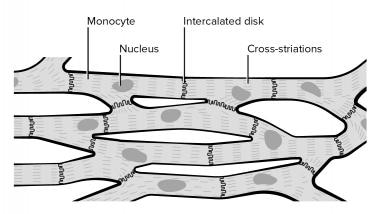
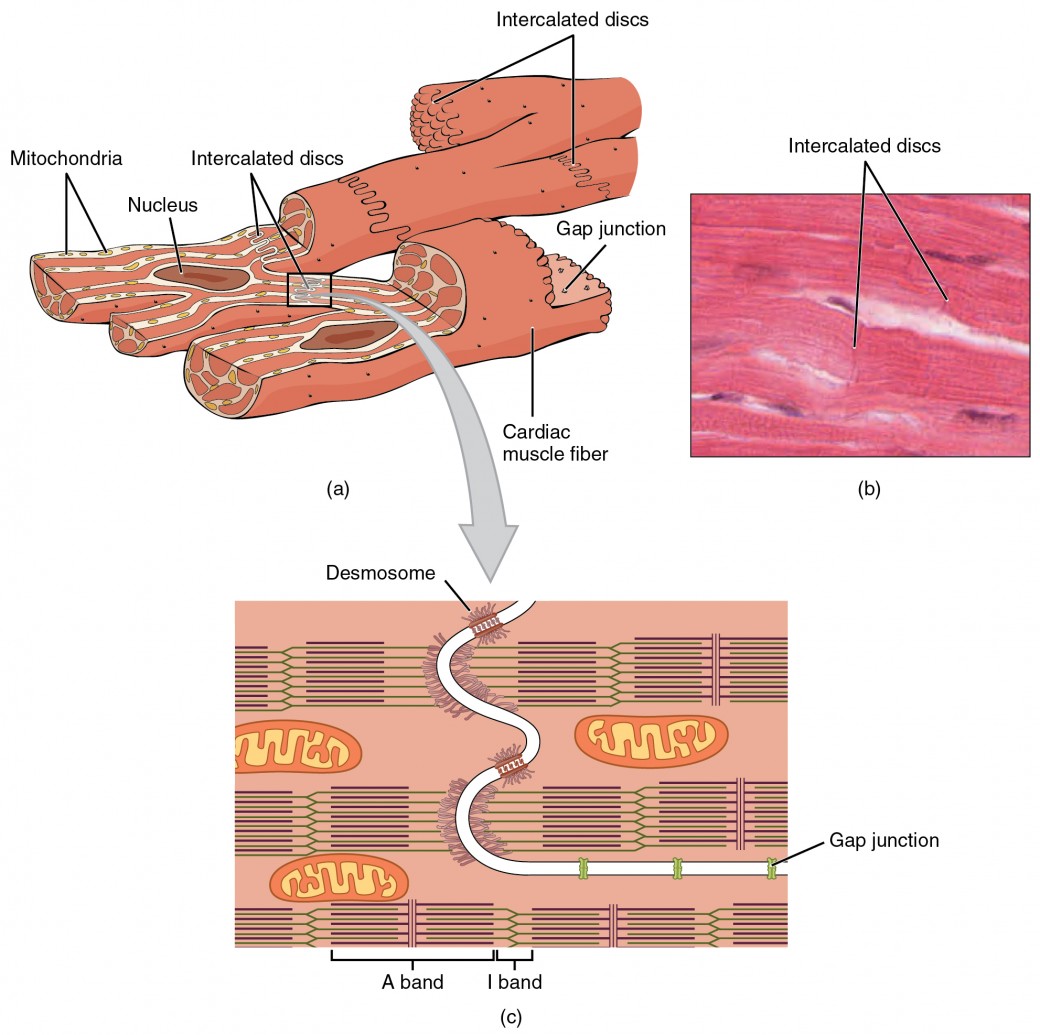
Cardiac Muscle Tissue | Anatomy and Physiology I A desmosome is a cell structure that anchors the ends of cardiac muscle fibers together so the cells do not pull apart during the stress of individual fibers contracting (Figure 2). Figure 2. Cardiac Muscle.

Cardiac muscle cell diagram
Structure of the cardiac muscle cell - ScienceDirect Structure of the Cardiac Muscle Cell* RICHARD J. STENGER, M.D.t and DAVID SPIRO, M.D., PH.D.Î Boston, Massachusetts IN 1664, the muscular nature of the heart was proclaimed in a monograph by Stensen [7]. Cardiac physiology at the cellular level: use of cultured ... Cardiac physiology at the cellular level: use of cultured HL-1 cardiomyocytes for studies of cardiac muscle cell structure and function Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol . 2004 Mar;286(3):H823-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00986.2003. Cardiac Muscle Diagram | Quizlet Start studying Cardiac Muscle. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
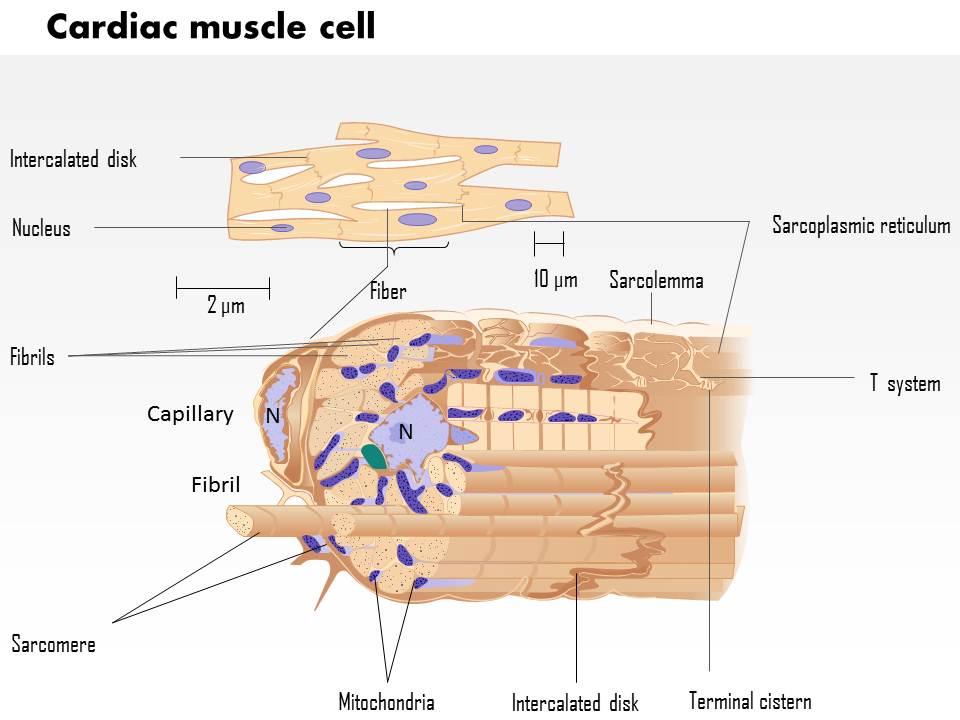
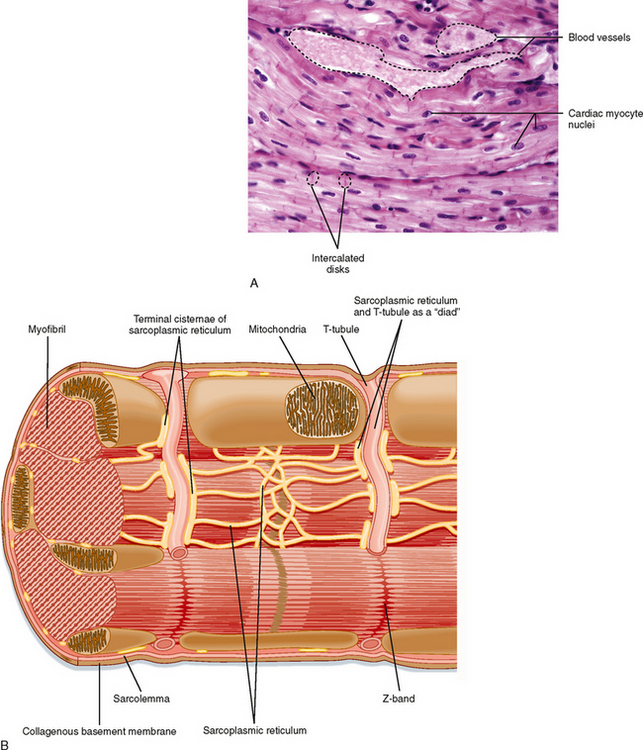
Cardiac muscle cell diagram. 19.2 Cardiac Muscle and Electrical Activity - Anatomy ... Figure 19.2.1 - Cardiac Muscle: (a) Cardiac muscle cells have myofibrils composed of myofilaments arranged in sarcomeres, T tubules to transmit the impulse from the sarcolemma to the interior of the cell, numerous mitochondria for energy, and intercalated discs that are found at the junction of different cardiac muscle cells. (b) A photomicrograph of cardiac muscle cells shows the nuclei and ... Structure of Cardiac Muscle - Myopathy - TeachMePhysiology Cardiac muscle is similar to skeletal muscle in that it is striated and that the sarcomere is the contractile unit, with contraction being achieved by the relationship between calcium, troponins and the myofilaments. This article will consider the structure of cardiac muscle as well as relevant clinical conditions. Overview of Basic Mechanisms of Cardiac Arrhythmia 1.3.2011 · The diagram shows a Purkinje bundle (D) ... recorded from the 3 cell types (current traces recorded during depolarizing steps from a holding potential of −80 mV to test potentials ranging between −20 and +70 mV). (D) ... specifically in cardiac muscle. Arch Inst Cardiol Mex. 1946; 16:205–65. ... PDF The cardiac muscle cell - Ecigclick The cardiac muscle cell Nicholas J. Severs Summary The cardiac myocyte is the most physically energetic cell in the body, contracting constantly, without tiring, 3 billion times or more in an average human lifespan. By coordinating its beating activity with that of its 3 billion neighbours in the main pump of the human heart, over
6.2 Cardiac Muscle and Electrical Activity - Fundamentals ... Figure 6.2.1. Cardiac muscle. (a) Cardiac muscle cells have myofibrils composed of myofilaments arranged in sarcomeres, T tubules to transmit the impulse from the sarcolemma to the interior of the cell, numerous mitochondria for energy, and intercalated discs that are found at the junction of different cardiac muscle cells. Basic Properties of Cardiac Muscle (With Diagram) | Humans ... ADVERTISEMENTS: The properties present in other muscle are also shown by the cardiac muscle. But it shows certain special features. 1. Rhythmicity: One of the main characteristic features of the cardiac muscle is that it can initiate its own impulse rhythmically. This inherent rhythmical property is present throughout the cardiac muscle as evident from the […] Cardiac Muscle Cell Model Diagram | Quizlet Start studying Cardiac Muscle Cell Model. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Cardiomyocytes (Cardiac Muscle Cells)- Structure, Function ... Although the regeneration of cardiac muscle cells was thought to be absent, studies have shown that these cells renew at a significantly low rate throughout the life of an individual. For instance, for younger people, about 25 years of age, the annual turnover of cardiomyocytes is said to be about 1 percent.
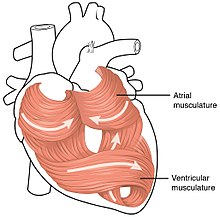
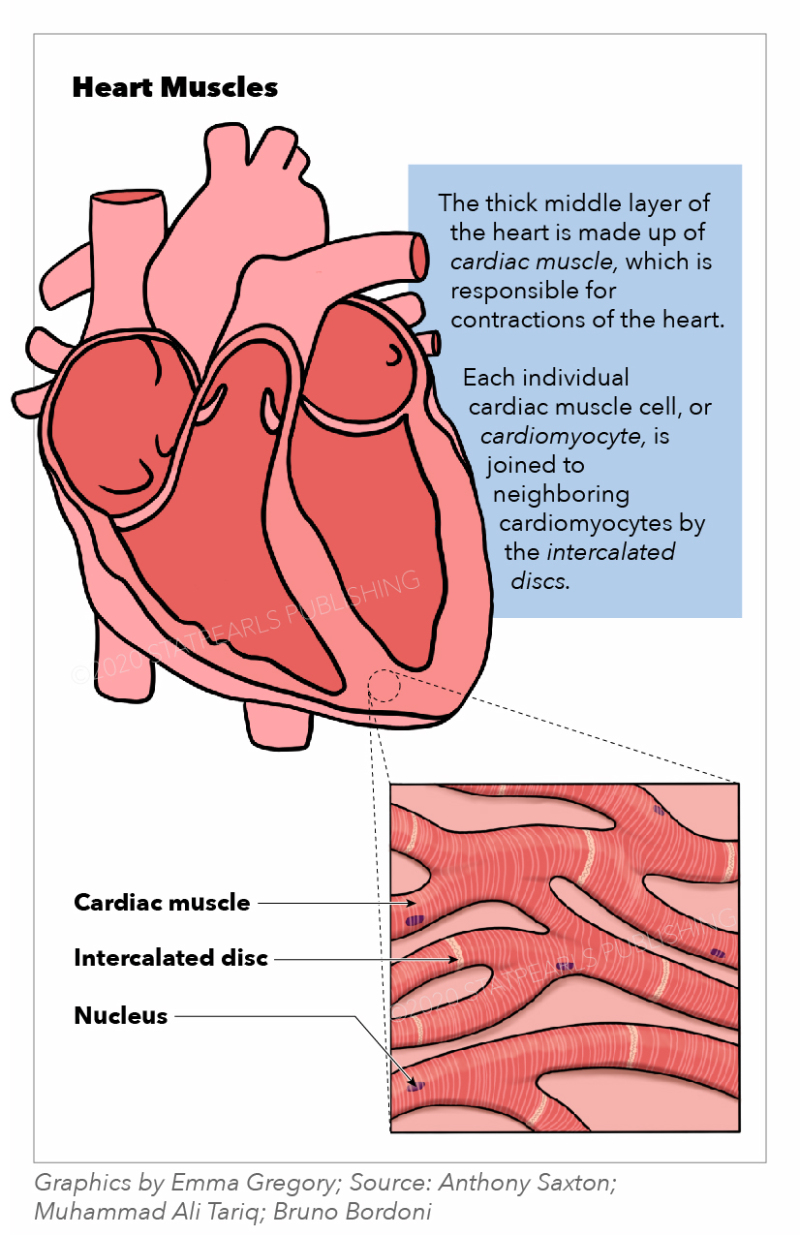
Muscles Notes: Diagrams & Illustrations | Osmosis NOTES NOTES MUSCLES MUSCULAR SYSTEM ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY osms.it/muscle-anatomy-physiology Three types of muscle cell/tissue Skeletal, cardiac, smooth Differ in location, innervation, cell structure All cells excitable, extensible, elastic SKELETAL MUSCLE Attaches to bone/skin; mostly voluntary; maintains posture, stabilizes joints, generates heat Most muscles consist of belly (contracts ... Cardiac Muscle - Cells, Structure, Function, Connection ... The above diagram shows the cross-section of the four-chambered mammalian heart. Cardiac Muscle Structure and Cardiac Muscle Function. Let us look at the Cardiac Muscle Function and Cardiac Muscle Structure in detail, here. Gross Anatomy. Cardiac muscle tissue is also called the myocardium, and forms the heart's bulk. Physiology, Cardiac Muscle - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf Cardiac muscle is a network of involuntary and striated tubular cardiomyocytes or cardiac muscle cells. These cardiomyocytes are joined end-to-end by a structure known as intercalated discs. Each myocyte contains a single nucleus and is surrounded by a cell membrane known as the sarcolemma. Cardiomyocytes (Cardiac Muscle Cells) - Structure ... Cardiac muscle cells or cardiomyocytes (also known as cardiac myocytes) are the muscle cells (myocytes) that make up the heart muscle. Cardiomyocytes go through a contraction-relaxation cycle that enables cardiac muscles to pump blood throughout the body. [In this image] Immunostaining of human cardiomyocytes with antibodies for actin (red ...
CARDIAC MUSCLE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION - Clinical Gate Describe the structural characteristics of cardiac muscle cells. 2. Discuss the role played by calcium ions in the regulation of cardiac muscle function. 3. Explain the ionic basis for the resting potential of the ventricular muscle cells. 4. List the characteristics of the pacemaker potential in sinoatrial and atrioventricular node tissue. 5.
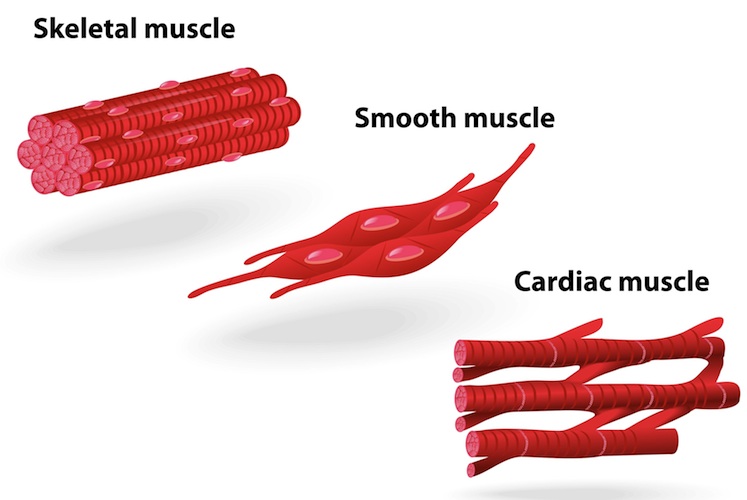
Difference Between Cardiac Muscle And Skeletal Muscle at ... Cardiac Muscle and Skeletal Muscles can be differentiated mainly based on their structure, functions and other features. Explore more differences at BYJU'S
Cardiac Ion Channels | Circulation: Arrhythmia and ... 1.4.2009 · In cardiac muscle, 2 types of Ca 2+ channels, the L- (low threshold type) and T-type (transient-type), transport Ca 2+ into the cells. The L-type channel is found in all cardiac cell types. The T-type channel is found principally in pacemaker, atrial, and Purkinje cells. The unqualified descriptor Ca 2+ channel refers to the L-type channel.
The cardiac muscle cell The cardiac myocyte is the most physically energetic cell in the body, contracting constantly, without tiring, 3 billion times or more in an average human lifespan. By coordinating its beating activity with that of its 3 billion neighbours in the main pump of the human heart, over 7,000 litres of bl …
Cardiac Muscle Tissue - Anatomy & Physiology A desmosome is a cell structure that anchors the ends of cardiac muscle fibers together so the cells do not pull apart during the stress of individual fibers contracting (). Cardiac Muscle Intercalated discs are part of the cardiac muscle sarcolemma and they contain gap junctions and desmosomes.
Cardiac muscle tissue: Definition, function, and structure Only cardiac muscle tissue, comprising cells called myocytes, is present in the heart. In this article, we discuss the structure and function of cardiac muscle tissue.
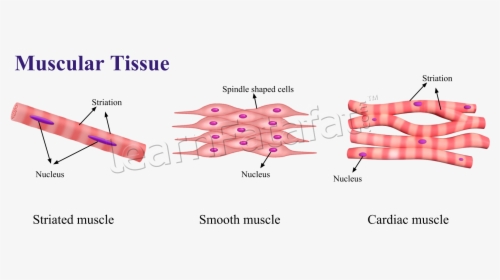
Striated muscle: Structure, location, function | Kenhub Cardiac musculature Structure of the cardiac muscle and fiber. A cardiac muscle cell (cardiomyocyte) is about 10-20 µm thick and 50-100 µm long. The cytoplasm contains myofibrils and densely packed mitochondria. The fibrils do not run strictly parallel to each other but rather branch in a complex pattern. The cardiac muscle cell has one centrally located nucleus.
Cardiac Muscle Tissue: Function, Structure, Conditions ... When one cardiac muscle cell is stimulated to contract, a gap junction transfers the stimulation to the next cardiac cell. ... Structure of cardiac muscle. (2018). teachmephysiology.com ...
Angina - Wikipedia Angina, also known as angina pectoris, is chest pain or pressure, a symptom of coronary heart disease, usually due to insufficient blood flow to the heart muscle (myocardium).. Angina is usually due to obstruction or spasm of the arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle. Other causes include anemia, abnormal heart rhythms, and heart failure.
Cardiac Muscle Tissue - Anatomy and Physiology A desmosome is a cell structure that anchors the ends of cardiac muscle fibers together so the cells do not pull apart during the stress of individual fibers contracting (). Cardiac Muscle Intercalated discs are part of the cardiac muscle sarcolemma and they contain gap junctions and desmosomes.
Cardiac Muscle - Definition, Function and Structure ... Cardiac Muscle Definition. Cardiac muscle, also known as heart muscle, is the layer of muscle tissue which lies between the endocardium and epicardium.These inner and outer layers of the heart, respectively, surround the cardiac muscle tissue and separate it from the blood and other organs. Cardiac muscle is made from sheets of cardiac muscle cells.
Cardiac muscle tissue histology - Kenhub Cardiac muscle tissue, also known as myocardium, is a structurally and functionally unique subtype of muscle tissue located in the heart, that actually has characteristics from both skeletal and muscle tissues.It is capable of strong, continuous, and rhythmic contractions that are automatically generated. The contractility can be altered by the autonomic nervous system and hormones.
Cardiac muscle - Wikipedia Viewed through a microscope, cardiac muscle cells are roughly rectangular, measuring 100-150μm by 30-40μm. Individual cardiac muscle cells are joined at their ends by intercalated discs to form long fibers. Each cell contains myofibrils, specialized protein contractile fibers of actin and myosin that slide past each other.
Lecture 6: Heart Anatomy and Cardiac Muscle Cell Structure Cardiac cell structure • Small discrete cells • Intercalated disks with desmosomes • Gap junctions = syncytium • Many mitochondria • Sr and t tubules • Striated Figure 12.7: Cardiac Muscle Cells Fig 12.8: Cardiac Conduction System Electrical Activity of the Heart Fig 12.10: Pacemaker Cell
Cardiac Muscle Tissue | Interactive Anatomy Guide Cardiac muscle cells have a branched shape so that each cell is in contact with three of four other cardiac muscle cells. Together all of the cardiac muscle cells in the heart form a giant network connected end to end. At the ends of each cell is a region of overlapping, finger-like extensions of the cell membrane known as intercalated disks. ...
Cardiac Muscle Diagram | Quizlet Start studying Cardiac Muscle. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Cardiac physiology at the cellular level: use of cultured ... Cardiac physiology at the cellular level: use of cultured HL-1 cardiomyocytes for studies of cardiac muscle cell structure and function Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol . 2004 Mar;286(3):H823-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00986.2003.
Structure of the cardiac muscle cell - ScienceDirect Structure of the Cardiac Muscle Cell* RICHARD J. STENGER, M.D.t and DAVID SPIRO, M.D., PH.D.Î Boston, Massachusetts IN 1664, the muscular nature of the heart was proclaimed in a monograph by Stensen [7].

















0 Response to "36 cardiac muscle cell diagram"
Post a Comment